Hello, homelab enthusiasts and network hackers!
Ever felt frustrated by the limitations of stock router firmware? I certainly have. On my trusty TP-Link Archer A6, the Guest Wi-Fi feature exists, but it offers zero options for bandwidth throttling. As soon as a guest or neighbor connects, the main connection suffers immediately.
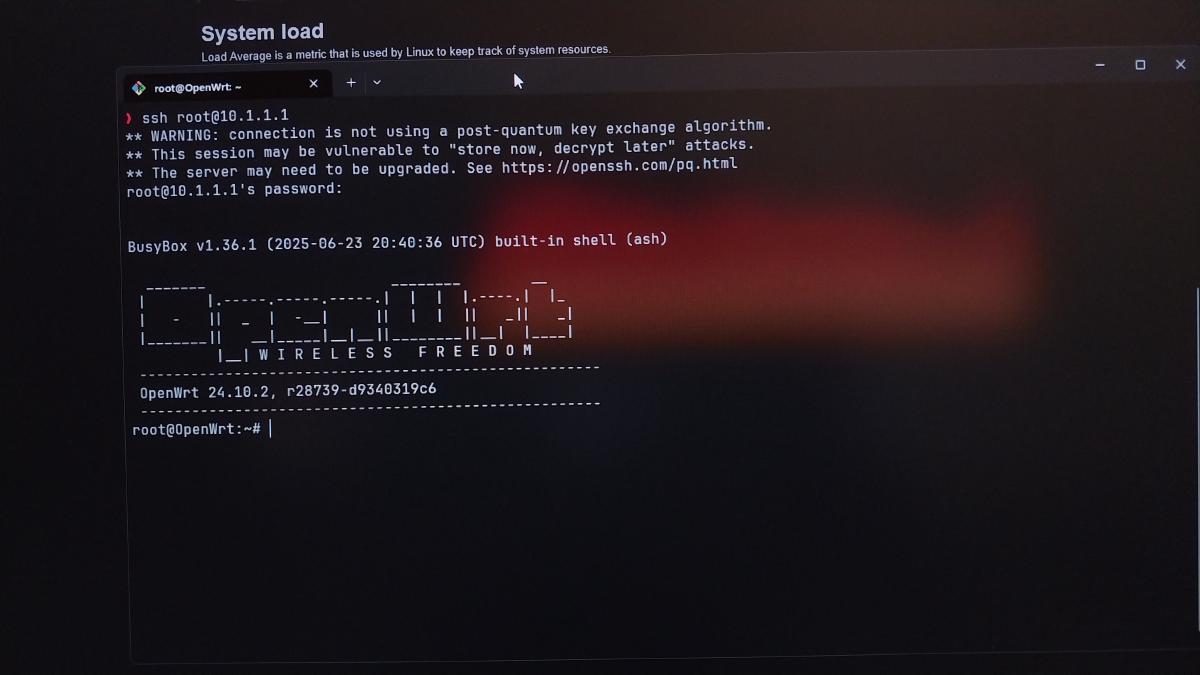
Eventually, I decided to flash it to OpenWrt. Initially, I tried the “industry standard” approach: SQM (Cake/FQ_Codel). The results? It was clean, but my Archer A6—which is a budget to mid-range router—started to struggle. After a few days, the router would hang and require a hard reboot. It turns out the packet encapsulation process in SQM is quite CPU-intensive for lower-end hardware.
I switched to a “closer to the metal” method: Native nftables in FW4. No heavy overhead, just lightweight scripting. The result? Weeks of stable uptime, a cool CPU, and perfect per-device limitation.
Here is a guide to Lightweight Per-Device (IP) QoS that is resilient even after power outages.
Why nftables? #
Unlike SQM, which manages complex packet queues, we use the limit rate feature directly within the nftables ruleset. This is extremely efficient because:
-
No SQM/CAKE: No CPU overhead from heavy queue management.
-
Per-Device: Every device in the Guest segment gets a fair, identical share.
-
FW4 Native: Integrated directly into the latest OpenWrt firewall system.
Step 1: Clean Up Old Traces #
Before starting, ensure there are no conflicts with other QoS packages. We want a clean firewall state.
# Remove old QoS packages if they exist
opkg remove luci-app-nft-qos nft-qos --force-removal-of-dependent-packages
rm -rf /etc/nftables.d
rm -rf /etc/config/nft-qos
nft flush ruleset
/etc/init.d/firewall restartStep 2: Create the Limitation Script #
We will create a rule where every IP in the 10.1.2.0/24 segment (Guest) is limited to 6 Mbps (approximately 750 KB/s).
mkdir -p /etc/nftables.d
cat << 'EOF' > /etc/nftables.d/guest-limit.nft
set guest_hosts {
type ipv4_addr
flags dynamic,timeout
timeout 5m
}
chain guest_prerouting {
type filter hook prerouting priority -150; policy accept;
ip saddr 10.1.2.0/24 add @guest_hosts { ip saddr }
ip saddr @guest_hosts limit rate over 750 kbytes/second drop
}
chain guest_postrouting {
type filter hook postrouting priority -150; policy accept;
ip daddr 10.1.2.0/24 add @guest_hosts { ip daddr }
ip daddr @guest_hosts limit rate over 750 kbytes/second drop
}
EOFStep 3: Register to the Firewall (FW4) #
To ensure OpenWrt runs this script automatically at boot, we must register it in the UCI firewall configuration.
uci add firewall include
uci set firewall.@include[-1].type='nftables'
uci set firewall.@include[-1].path='/etc/nftables.d/guest-limit.nft'
uci commit firewall
fw4 reloadStep 4: “Blackout” Protection (Auto-Heal) #
A classic OpenWrt issue on smaller routers is filesystem corruption or firewall load failure after a sudden power loss. We’ll create a simple watchdog in rc.local.
cat << 'EOF' > /etc/rc.local
#!/bin/sh
# Check if firewall is active; if not, force a restart
nft list table inet fw4 >/dev/null 2>&1 || {
logger -t fw4-watchdog "Firewall missing, auto restore in progress..."
/etc/init.d/firewall start
fw4 reload
}
exit 0
EOF
chmod +x /etc/rc.localResult Analysis #
Once this configuration is active, you can verify it by running nft list table inet fw4 | grep guest. If it appears, congratulations! Your router now has a highly efficient “traffic cop.”
| Feature | Result |
|---|---|
| CPU Load | Extremely Low (Idle near 0%) |
| Limitation | 6 Mbps per IP (Stable) |
| Resilience | Survives Reboots & Power Outages |
Troubleshooting: What Could Go Wrong? #
While this method is stable, the world of “modding” always has variables. Here are some common issues:
1. Wi-Fi Connected but No Internet #
-
Cause: Usually occurs if the
fw4table fails to load perfectly due to internal conflicts. -
Solution: Run this quick fix command in the terminal:
cp /rom/etc/init.d/firewall /etc/init.d/firewall chmod +x /etc/init.d/firewall /etc/init.d/firewall start fw4 reload
2. Limit Not Working (Still Full Speed) #
-
Cause: Guest devices might be receiving IPs outside the
10.1.2.0/24range. -
Solution: Check Network > Interfaces and ensure your Guest interface uses the IP segment defined in the script. If different, adjust the values in
/etc/nftables.d/guest-limit.nft.
3. Software Flow Offloading Issues #
-
Cause: The Software Flow Offloading feature sometimes bypasses nftables to increase throughput.
-
Solution: If the limit isn’t working, try disabling “Software Flow Offloading” under Network > Firewall. However, on the Archer A6, this feature can usually coexist with nftables limits.
With this method, my TP-Link Archer A6 can now serve guests peacefully without interrupting my gaming sessions on the main network. A light router makes for a peaceful mind.