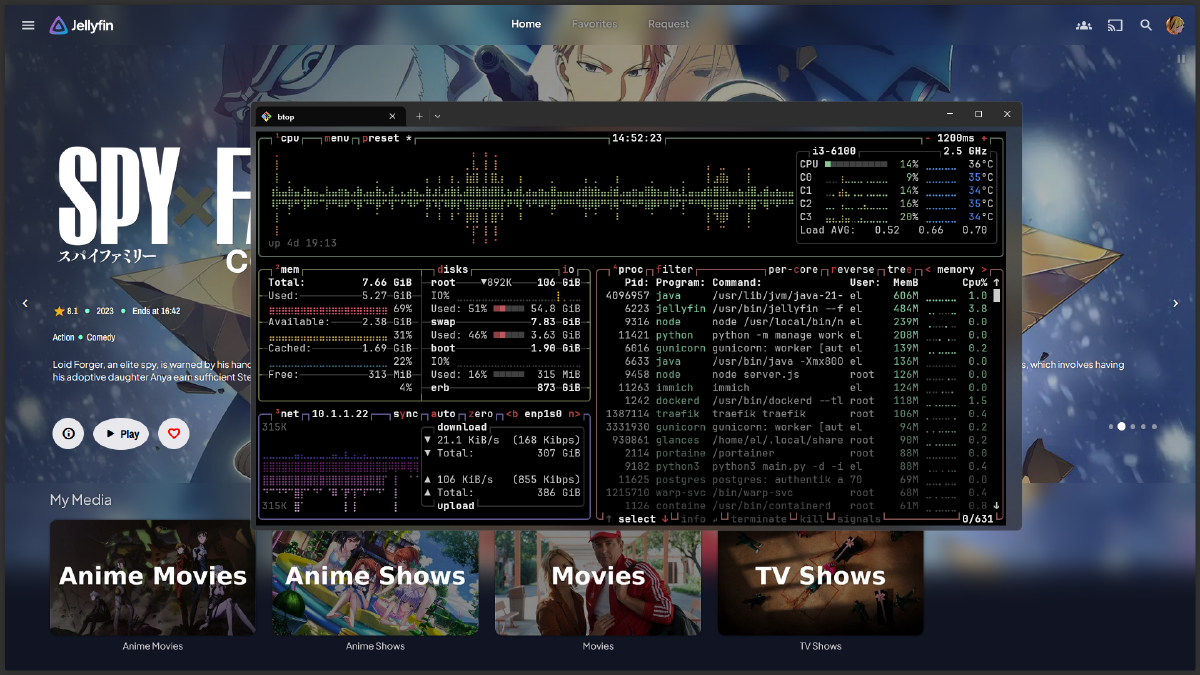
Have you ever noticed your Linux server or laptop slowing down after a few days? If you use Cloudflare WARP or Cloudflare Zero Trust, the culprit might be the warp-svc.service.
Many users have reported a Cloudflare WARP memory leak phenomenon, where RAM usage continuously swells over time. In some cases, after just 4 days of uptime, memory consumption can hit 800MB to 1GB, which significantly compromises system stability.
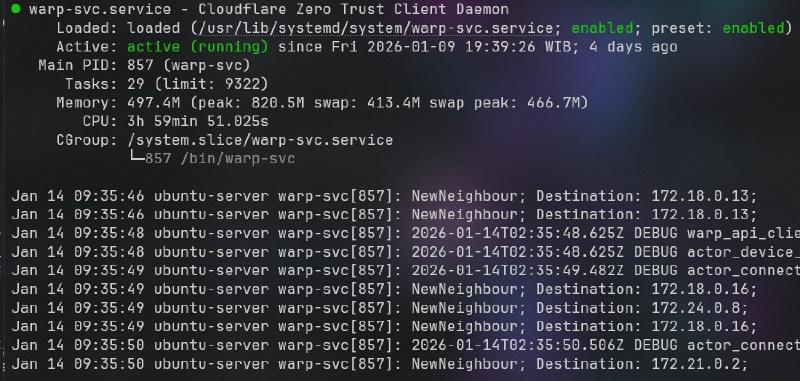
In this tutorial, we will discuss practical steps to resolve this issue using an auto restart mechanism via systemd timer every 6 hours. This is the most effective solution to keep resource usage low without requiring manual intervention.
Prerequisites #
Before starting the configuration process, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- Sudo or Root access on your Linux system.
- Cloudflare WARP or Cloudflare Zero Trust (
warp-svc) already installed. - Basic familiarity with terminal text editors (such as
nanoorvim). systemdservice active (standard on Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and most modern distros).
Step-by-Step: Configuring warp-svc Auto Restart #
Follow these steps to create an automated mechanism that refreshes Cloudflare WARP periodically.
Step 1: Create the Restart Service Unit #
The first step is to create a service unit file that will execute the restart command. This unit is a oneshot type, meaning it runs once every time it is triggered.
Create a new file with the following command:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/warp-svc-restart.serviceInsert the following code:
[Unit]
Description=warp-svc auto restart
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/bin/systemctl restart warp-svc.serviceTechnical Explanation: This file acts as a “work instruction.” The ExecStart line commands the system to perform a restart on the main Cloudflare WARP service.
Step 2: Create the Timer Unit #
Once the instruction is ready, we need a scheduler or “alarm” to trigger that instruction automatically every 6 hours.
Create the timer file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/warp-svc-restart.timerInsert the following code:
[Unit]
Description=Restart every 6 hours
[Timer]
OnBootSec=5min
OnUnitActiveSec=6h
Unit=warp-svc-restart.service
[Install]
WantedBy=timers.targetTechnical Explanation: * OnBootSec=5min: Delays the first execution for 5 minutes after the system starts (to avoid interfering with the booting process).
OnUnitActiveSec=6h: Reruns the service every 6-hour interval.Unit=: Links this timer to the service file we created in Step 1.
graph TD
A[Linux System Booting] --> B{Timer Active?}
B -- Yes --> C[Wait 5 Minutes
OnBootSec]
C --> D[Trigger Service:
warp-svc-restart.service]
D --> E[Execute Command:
systemctl restart warp-svc.service]
E --> F[RAM Memory Freed]
F --> G[Wait 6 Hours
OnUnitActiveSec]
G --> D
subgraph Systemd Engine
D
E
end
subgraph Final Result
F
end
Step 3: Enable and Start the Timer #
Finally, we need to reload the systemd configuration so the new files are recognized, then activate them.
Run the following commands one by one:
# Reload daemon to recognize new files
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# Enable to run automatically at boot
sudo systemctl enable warp-svc-restart.timer
# Start the timer now
sudo systemctl start warp-svc-restart.timerTo verify the timer is active and see the next scheduled execution, use:
systemctl list-timers --all | grep warpAdditional Technical Insights #
Why Does the Memory Leak Happen? #
A memory leak in system-level applications like warp-svc usually occurs due to imperfect memory allocation management within the source code. In the context of Cloudflare WARP, this application handles thousands of data packets and encryption tasks every second. If certain variables or objects in the code are not “cleaned up” after use, that memory remains locked and accumulates.
Technically, Cloudflare Zero Trust utilizes a modified WireGuard protocol. Under certain network conditions, repetitive handshakes or connection failures can cause background logging or state management processes to consume abnormal amounts of resources. Without a restart, the operating system cannot reclaim that memory from the application.
Impact and Network Context #
Restarting the service every 6 hours has minimal implications on connectivity. The service restart process usually takes less than 2 seconds. However, during that brief moment, your VPN connection will drop momentarily (a micro-interruption). If you are using a server for highly sensitive real-time applications, ensure this 6-hour interval does not clash with your peak operational hours.
Conclusion #
A Cloudflare WARP memory leak reaching 800MB or more can significantly hinder performance. By implementing a systemd timer to automatically restart warp-svc.service every 6 hours, you ensure RAM usage remains stable without having to monitor the terminal every day.
Simple Troubleshooting #
If the service fails to restart, ensure:
- The path
/usr/bin/systemctlis correct (check withwhich systemctl). - There are no typos in the service name
warp-svc.service. - Check error logs using
journalctl -u warp-svc-restart.service.
Are you experiencing issues implementing this configuration? Or do you have an even more efficient solution? Share your questions and experiences in the comments below!